Jump Ahead
Peak shaving, also known as peak load shaving is a technique businesses use to reduce their electricity expenses. It is beneficial for reducing costly demand charges, often known as capacity charges or capacity tariffs. These capacity loads are determined by the maximum peak load of electricity consumed which amounts to a significant portion of the utility bill.
Businesses and other major electricity consumers regulate their energy consumption to minimize temporary surges in demand, hence reducing these charges. With regulation of their electricity usage pattern, these businesses efficiently reduce the peaks. It results in decreased demand charges and substantial cost savings.
Why Is Peak Shaving Necessary?
Companies that offer electric vehicles’ charging, or use heavy machinery, heating boilers or operating heat pumps have a high energy demand. Commercial and industrial businesses keep records of the spikes in energy consumption using a registered load profile. Registrierte Leistungsmessung (RLM) in Germany assists in managing this load profile by transmitting data every 15 minutes.
The load peaks pose challenges for businesses as they result in increasing energy costs and unstable grids. This necessitates load management such as peak shaving for reducing these costly peak loads and capacity charges.
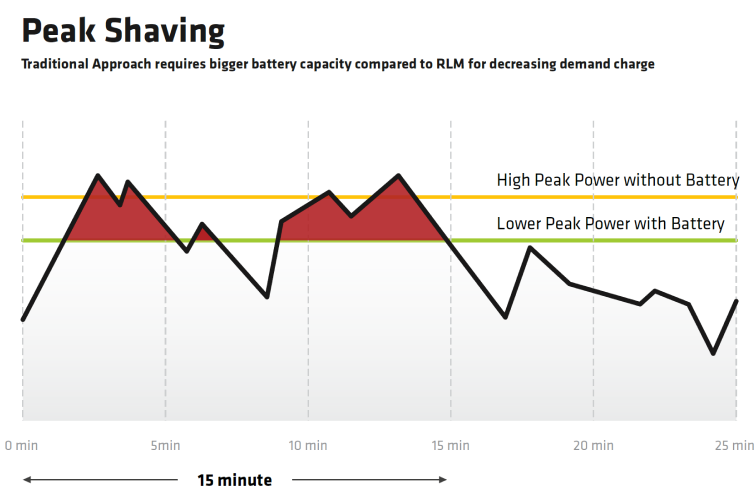
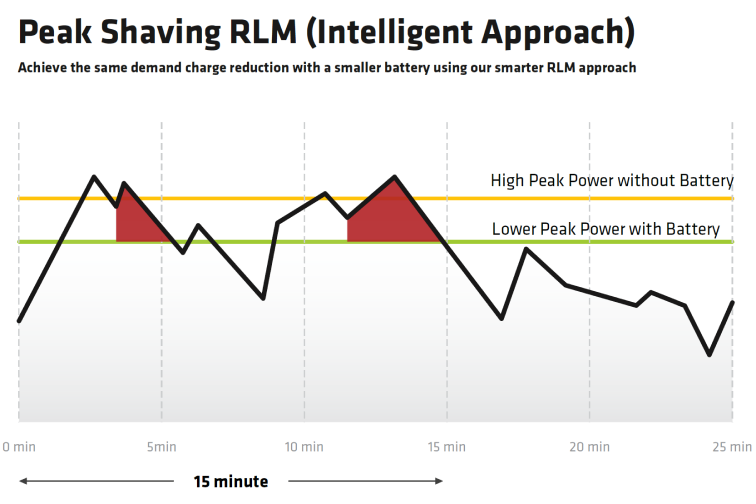
What’s the Difference Between Peak Shaving and Load Shifting?
Peak shaving means a reduction of power consumption to avoid load spikes and high demand charges in the electricity bill. This is attained by either lowering consumption or from an additional local power source like rooftop photovoltaic (PV) system, batteries or bidirectional electric vehicles as well.
Whereas, load shifting is a technique of electricity consumption where electricity usage is moved to the periods of lower power prices or reduced temporarily. Load shifting is suitable for flexible loads as it allows easy shifting without impacting overall operations such as charging electric vehicles.

How Does Peak Shaving Work?
Peak shaving can be achieved by either demand-side or supply-side management.
Demand-side management aims to reduce demand through various strategies’ implementation. For example, in the e-mobility use case, an energy management system can automatically limit the amount of electricity given to the charging infrastructure of electric vehicles. In industrial settings, the usage of unwanted or unnecessary heavy machinery can be discontinued temporarily, when the required power is aiming to cross the desired power limit.
Local power sources are used in supply-side management to lower the reliance on the electrical grid during peak hours. Integrating energy sources is significant in achieving this like solar panels, batteries or fuel cells. Backup generators, a fossil fuel-powered option can also be used for this purpose but their emission is quite high.
The purpose of demand and supply side management is the same as they reduce the load at the grid connection point, effectively lowering peaks. Both management sides can either be applied separately or together to achieve this.
What Are the Benefits of Peak Shaving?
The primary benefit of peak shaving is that it reduces grid fees through 15-minute optimization. HIS-EMS peak shaver module optimizes charging events and reduces expenses by trimming peak loads.
The peak shaving algorithm takes daily estimates of local production and consumption and monitors them in 15-minute intervals, which Distribution System Operators (DSOs) use to bill peak power use.
The algorithm of peak shaving estimates and monitors local production and energy consumed in 15-minute intervals daily. This record is used by Distribution System Operators (DSOs) to bill the peak power use. Within the optimization interval, the real-time residual and building load are considered, and each linked device’s power requirement is dynamically modified.
The value defining the peak load capacity is based on the average power value and is defined by cost-relevant for a 15-minute interval. The grid fee is minimized by power optimization that flows during a 15-minute time window. Grid operators can reduce energy costs by maintaining steady loads. Long-term pricing is often determined by the largest peak inside a given time frame, therefore a single 15-minute period with exceptionally high power demand can dictate costs for an entire year.

Best Peak Shaving Practices
Evaluation of Load Profile
The load profile analysis of a site highlights the patterns of electricity consumption over time. This helps in the identification of the precise amount and timing of peak shaving based on previous data. The magnitude of demand fluctuation such as load variability must also be considered during the entire day. Sites with higher load variability must leverage a flexible and smart energy management system.
Selecting Right Energy Storage Tech
An energy storage system is not required to reduce peaks but it’s beneficial from the supply management side. To choose the right energy storage tech certain variable factors like cost, performance, life span, safety and environmental footprint must be considered. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are versatile and easier to install which makes them popular for peak shaving operations.
Defining Your Objectives
Peak shaving can be used for different objectives. For this, operators have to set their priorities right regarding minimizing electricity costs, improving grid stabilization or reducing emissions. This ultimately defines the logic used in the control strategy of the energy management system for reducing peak power.
This helps in determining if the scheduled or predictive control is applied. Schedule control operates on a predefined schedule of charging and discharging and it depends on the load profile and tariff structure of a site.
On the other hand, predictive control optimizes charging and discharging based on historical and real-time data or load and grid forecasts. All energy assets in the system will be controlled and monitored regardless of particular objectives. They are monitored and controlled in real-time and their load optimization is based on user-defined peak thresholds.
Peak Shaving In Practice
Sites with significant flexible loads benefit from peak shaving the most. Consider a use case of electric vehicle (EV) charging.
Sample Peak Shaving Calculation
As has been highlighted previously, grid operators charge their fees based on a site’s highest peak power, even if they do not occur frequently. The estimation for a high-power charging facility reveals that all charge points are used for an average of 11 minutes every day. This period determines the price as grid connections are designed for peaks.
If at a site six EVs are required to be charged simultaneously with six DC Chargers with each having 150 kilowatts, grid operators would charge this site a maximum demand charge of 900 kW for electricity consumed.
On the other hand, if the site has to charge six EVs at the same time with DC Chargers, 150 kilowatts each, the maximum demand charge by grid operators would be 900 kW for electricity used. Assuming a price of €110 per kW, the maximum demand charge would be €99,000.
In this case, the peak shaving algorithm can lower the power delivered to each charge point to 100 kW. This helps in reducing the demand charge by one-third to 600 kW or €66,000.
This results in charging EVs to their full capacity within minimum grid constraints, hence enabling Charge Point Operators (CPOs) to avoid energy rates by one-third and reduces the CAPEX as in this case the transformer size at the grid connection also decreases.
Case Study for High Power Charging
If your charge point operator powers up electric cars / trucks up to 300 km of range in 15 minutes and has charge points of 300 kW, this increases grid fees if the charge points are not used for at least 7 hours daily at maximum power . Although this solution is convenient it results in huge peak loads which ultimately increase grid fees.
To deliver clients a fast charging solution, and also to reduce power usage and fees, Charge Point Operators can use HIS-Energy’s battery energy storage system (BESS). Our Battery Management System intelligently distributes power among charge points to reduce peaks and peak power fees without compromising convenience.
The Future of Peak Shaving
Peak shaving is being recognised in the world for its financial gains for businesses as well as for energy regulation and grid stability. Currently, peak shaving is considered a primary business and industry tool but soon it will extend to private households.




